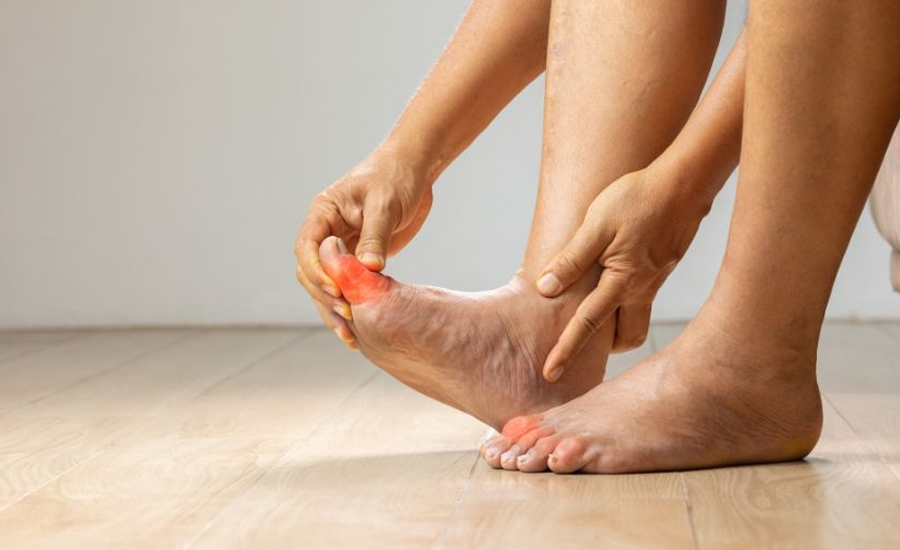
Gout is a form of arthritis that results in a sudden and intense joint pain, joint inflammation, and joint heat. It commonly occurs in the first MTP joint but can also involve other joints, such as the ankle, knee and wrist joint. Gout occurs when there is high levels of uric acid in the blood, which then deposits small, needle-like crystals in the joints. These crystals, in turn, bring about inflammation, which leads to pain and other discomforts. The persons having gout develop complications, which are referred to as gout flare. They developed as signs, and after three days at most, they regress.
Gout foods include red meat, seafood, sugary products and alcohol, but individuals with gout are discouraged from taking them. Anyone who is obese, or who has other medical conditions that affect arteries, is also at greater risk of developing the condition. The treatment of gout consists of drugs aimed at controlling the symptoms of the disease. It also consists of all those changes in behavior like taking proper and healthy food and must be in proper weight. Patient should follow the following instructions to avoid future out break: Increases water intake and avoid foods that are high in purine.
What is the Main Cause of Gout?
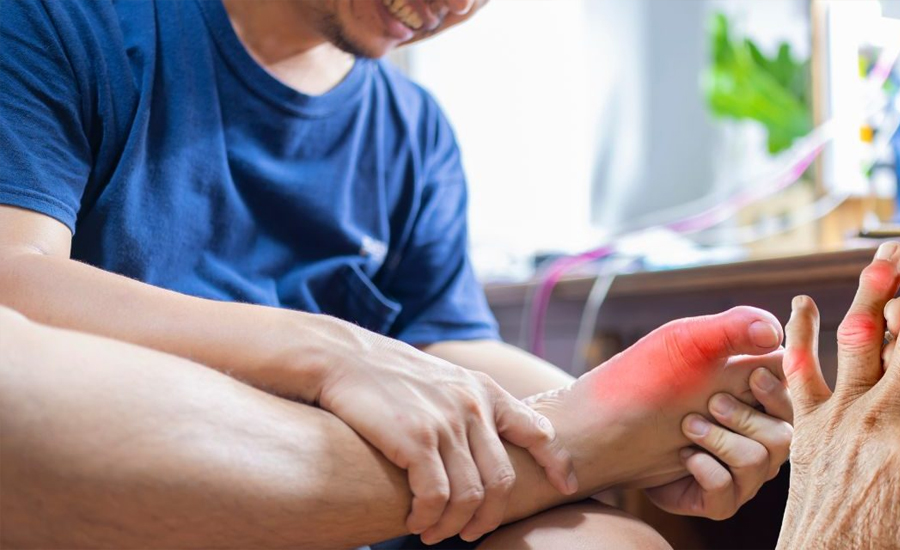
Gout is a type of arthritis that aims millions of individuals all over the globe. It is a disorder marked by sharp, intense pain, which commonly affects the joint of the big toe; however, other joints are not spared. Acquiring knowledge on the causes of gout is crucial in the prevention and handling of a flare. In the next sections, we elaborate on the fundamental determinant of gout and the related variables.
1. Excess Uric Acid in the Blood
The main cause of arthritis is the deposit of uric acid in the blood. These are for instance in some foods and drinks. Commonly, uric acid can be dissolved in the blood. It is metabolized through the liver, the excess removed by the kidneys and out through the bladder as urine. However, if there is excessive synthesis of the substance by the body or if the kidneys remove it in low quantities, gout occurs. Monosodium urate crystals form acute gouty arthritis in the form of sharp crystals in the joints.
2. Diet High in Purines
Foods rich in purines contribute to high levels of uric acid. Red meats, organ meats, shellfish, and some fish are high in purines. This includes anchovies and sardines. Eating these foods in excess raises uric acid, increasing gout risk.
3. Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol, especially beer and spirits, is another significant trigger for gout. It contains purines. It also interferes with the body’s ability to remove uric acid. Drinking alcohol can raise the risk of a gout attack.
5. Genetics
Family history can be a contributing factor to gout. A family history of gout may increase the risk of it.
7. Medical Conditions
Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease can raise gout risk. These conditions hinder the body’s uric acid regulation process. Knowing the main causes of gout can help. It can guide lifestyle changes to reduce flare-ups and manage symptoms.
Early-stage gout symptoms
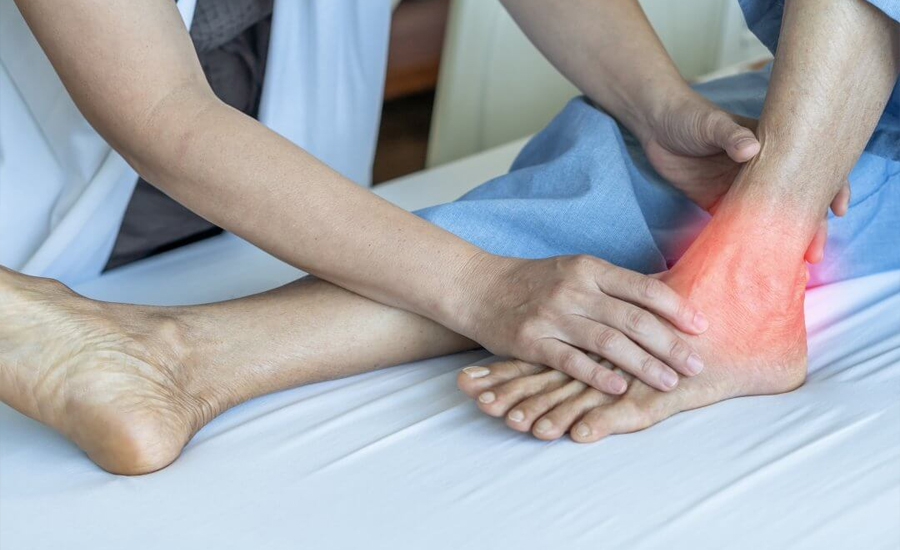
Gout unfolds as a type of arthritis through gradual progression. It’s vital to recognize the early symptoms. It helps in treating and preventing worse attacks. Early-stage gout may not always be obvious. But, it presents key signs that can indicate its onset. Below are the early symptoms of gout and what to watch for.
1. Mild Joint Pain
One of the first signs of gout is mild joint pain, often in the big toe. This pain may come and go and is usually manageable at first. As gout progresses, the pain can become severe and constant. This signals a need for medical attention.
2. Swelling in the Affected Joint
Swelling is another common symptom of early-stage gout. The affected joint exhibits swelling, reddening, and increased heat. Tenderness can accompany this, making touching or moving the joint uncomfortable.
3. Stiffness in the Joint
Gout seizes the affected joint, hindering normal movement with rigidness. This stiffness often appears in the mornings or after periods of rest. It may not alarm at first. But, persistent stiffness could signal early gout.
5. Discomfort at Night
Gout symptoms worsen at night. Many people feel pain in the affected joint while trying to sleep. The body’s lower temperature during sleep may cause uric acid to crystallize. This may lead to nighttime flare-ups.
Recognizing these early symptoms can help people seek treatment. It can also prompt lifestyle changes to prevent gout from worsening.
Gout Treatment
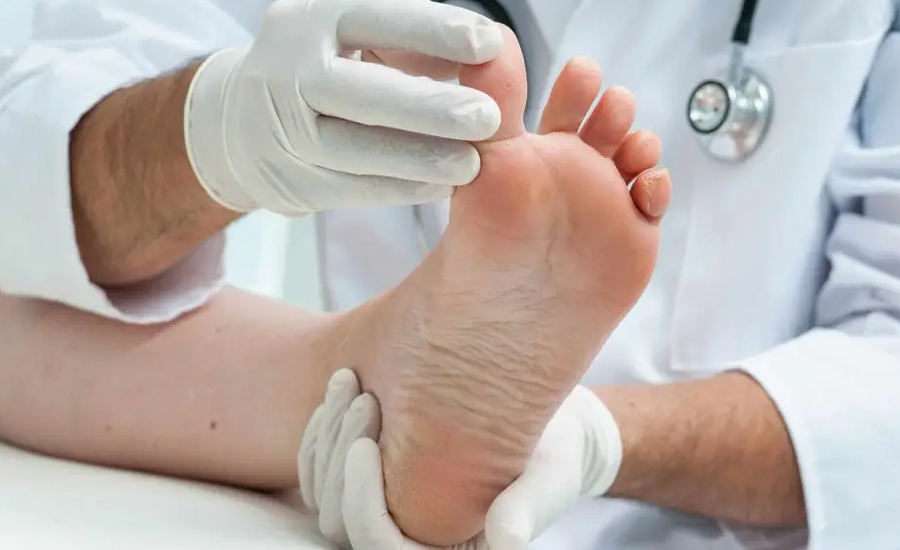
Gout is a painful condition. If untreated, it can disrupt daily life. Treatments that work offer assistance. They can manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and prevent long-term joint damage. Below are the key treatment options for gout.
1. Medications for Pain Relief
An important part of the treatment which is usually taken when the person is first diagnosed with gout is to deal with the pain during an attack. Other drugs including non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are commonly prescribed to help with pain and inflammation. In some bad instances, the doctor will recommend use of corticosteroids or colchicine to improve symptoms.
2. Uric Acid-Reducing Medications
Herbal medicines may be taken for illness as well as Doctors may recommend certain drugs. One way in which they work is that they reduce uric acid in the blood. Thus, allopurinol and febuxostat are the most familiar drugs in this category. They also inhibit the synthesis of uric acid. Probenecid increases the activity of kidneys that eliminate the surplus of uric acid. The above medications are useful in the sense that they may assist in avoiding future bouts of the same.
3. Dietary Changes
It can be noted that a low-purine diet is crucial and should be followed strictly when sufferer from gout. Reduction of consumption of foods that have high amounts of purine will reduce instances of gout. They are; Red meat, organ meat, seafood especially shellfish, and alcohol. A person should be taking a lot of vegetables, whole grain foods and low fat products such as dairy products. Lastly, ensure that you take more water so as to wash out uric acid from the body.
4. Weight Management
Overweight is another factor that must also be controlled during the management of gout. Obesity provides an environment with increased predispositions to gout. Thus, part control and exercise can minimize the manifestations and prevent the exacerbations of the disease.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
There are other factors which can be controlled to an extent and manage gout: There are dietary and weight management programs that can be followed for controlling gout. drink no alcohol during training and make sure to keep well hydrated. Also, the gout could be controlled by exercise, stress and adequate rest. Living happily with gout is probable within the purview of meds and approaches to daily living. It affords everyone a pain-free existence.
10-minute gout cure
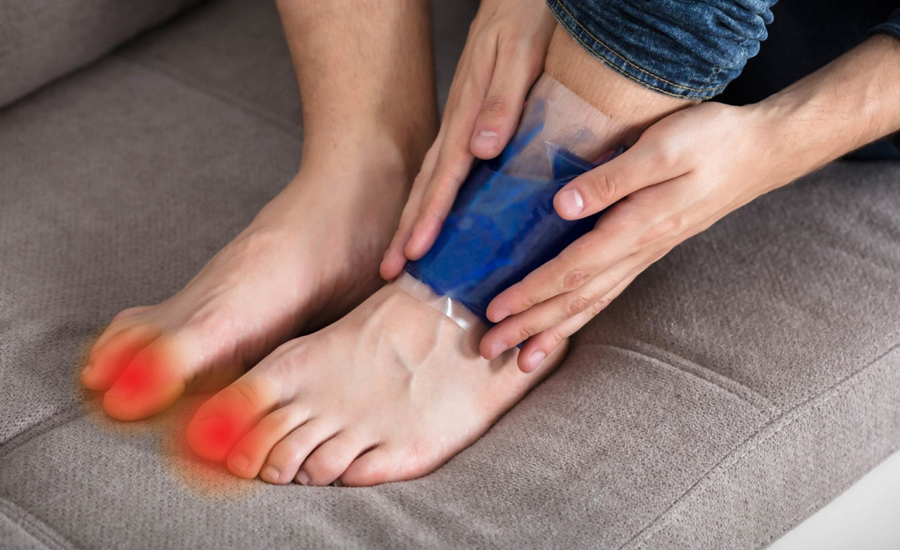
Gout is a form of arthritis, in which excess crystals of uric acid deposit in the joints thus making it painful. Even for all the treatments of gout, the promise of 10 minutes cure implies that the given treatment is a mere to go. As we earlier pointed out, gout is a chronic disease. It requires constant treatment with tablets, changes in regimen and dietary table No 5. I want to stress that there is what one can do to alleviate the discomfort in 10 minutes during a flare-up.
1. Cold Compress for Instant Relief
Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the affected joint can provide quick relief. The cold temperature helps reduce inflammation and numbs the area, easing the pain. Apply the compress for 10 minutes at a time, repeating as needed.
2. Elevation to Reduce Swelling
If gout affects your foot, ankle, or knee, try elevating the joint above heart level. It can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow. By keeping the joint raised, you may experience relief from pressure and discomfort.
4. Gentle Massage
A light massage of the joint may relieve some tension and discomfort. Be gentle, as the area is likely sensitive, but this can encourage blood flow and promote healing.
5. Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
An over-the-counter anti-inflammatory like ibuprofen can help. It can reduce pain and inflammation within 10 minutes. This provides temporary relief but won’t manage gout long-term. While these methods can help short term, consult a doctor for proper gout treatment.
What Causes Gout in Females?
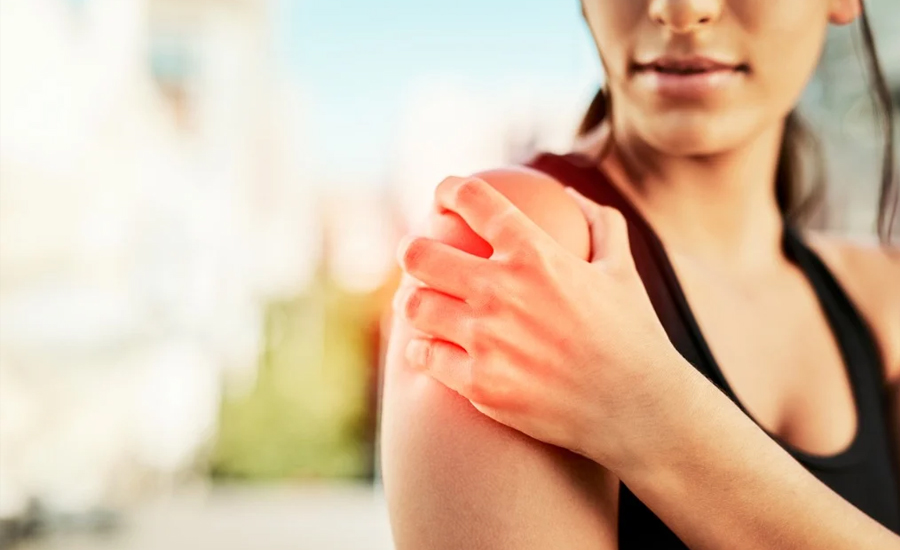

Gout is often seen as a man’s disease. But, women can also get it, especially after menopause. It is a painful form of arthritis. Both hormonal changes and lifestyle factors cause gout in females. Understanding the key triggers can help in preventing and managing the condition.
1. Hormonal Changes Post-Menopause
Before menopause, estrogen helps women remove uric acid. This lowers the risk of gout. After menopause, estrogen levels drop, leading to a higher buildup of uric acid in the blood. This increase makes women more vulnerable to developing gout as they age.
2. Diet and Lifestyle
Like men, women are at risk of gout if their diet is high in purines. Foods such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol can raise uric acid levels. Obesity is another factor. It raises uric acid, which strains the joints.
3. Medical Conditions and Medications
Some medical conditions can raise uric acid levels. They are kidney disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Some medications, like diuretics and aspirin, increase gout risk in women. They affect how the body processes uric acid.
By understanding these causes, women can take steps to manage gout more effectively
What causes gout in feet?
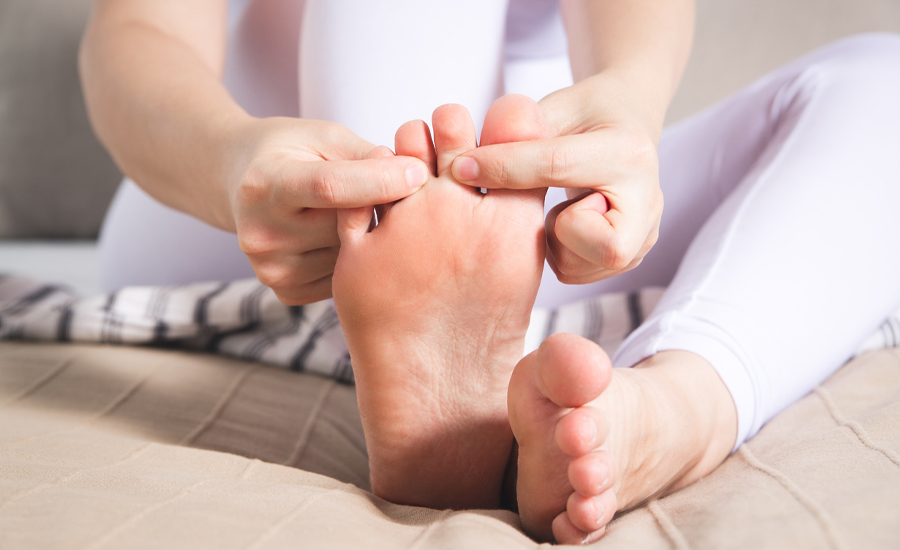

Gout targets the feet, focusing on the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe. This painful condition occurs when uric acid builds up in the body and forms crystals in the joints. Gout in the feet has several causes. Knowing them can help manage symptoms.
1. Uric Acid Crystals
The primary cause of gout in the feet is the formation of uric acid crystals. These sharp crystals collect in the joints, especially the toes. They cause intense pain, swelling, and redness.
2. Temperature and Blood Flow
Feet are more prone to gout. They are farther from the heart. Blood flow is slower, and the temperature is lower. These conditions make it easier for uric acid to crystallize and settle in the joints of the feet.
3. Pressure on Joints
Excessive walking, standing, or tight shoes can pressure the foot joints. This may increase the risk of gout flare-ups there. Managing stress on the feet can help reduce attacks.
How to treat gout on foot
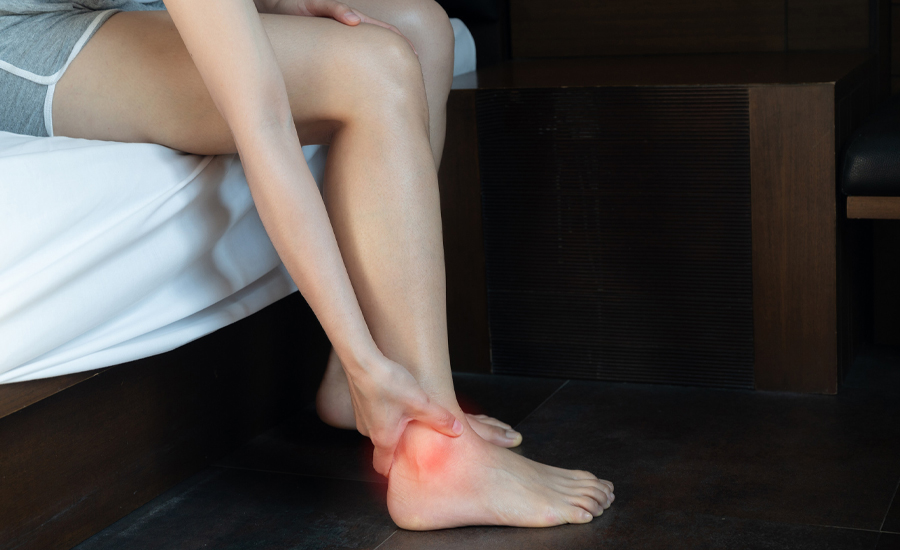
Gout in the foot, especially in the big toe, can cause severe pain, swelling, and discomfort. Address joint symptoms immediately to prevent permanent harm. Three methods treat gout in the foot with optimal results.
1. Rest and Elevation
Resting the affected foot is essential for managing gout symptoms. Keep the foot elevated to reduce swelling and improve blood circulation. Don’t strain the joint. Wear supportive shoes to avoid irritation.
2. Cold Compresses
A cold compress or ice pack can help the sore joint. It reduces inflammation and numbs the pain. Use the cold pack for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce discomfort and control swelling.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful form of arthritis. It often affects the big toe but can impact other joints as well. Effective management includes medications to control pain and lower uric acid. It also requires lifestyle changes. Add a low-purine diet and a healthy weight. Early symptom recognition and prompt treatment can prevent severe flare-ups and joint damage. With the right approach, people can manage gout and live well.
FAQs
What is the best medicine for gout?
The best medicines for gout are NSAIDs, like ibuprofen. Also, colchicine is effective for inflammation, and allopurinol for lowering uric acid. Consult a doctor to choose the right treatment.
What food causes gout?
High-purine foods can trigger gout by raising blood uric acid. These foods include red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and sugary drinks.
How to treat gout in the knee?
Treat gout in the knee with NSAIDs for pain. Rest and elevate the leg. Use cold compresses for swelling. Take uric acid-lowering meds as prescribed by a doctor.
Which food can reduce uric acid?
Foods that can help lower uric acid include cherries, low-fat dairy, whole grains, vegetables. Also, drink plenty of water. Avoid high-purine foods.

As a versatile and creative content writer, I craft compelling narratives that captivate and engage readers. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for storytelling, I transform ideas into impactful content. Clients choose me for my ability to understand their vision, deliver high-quality work on time, and provide a unique voice that resonates with their audience.

